Data Privacy and Smart Home IoT Vendors

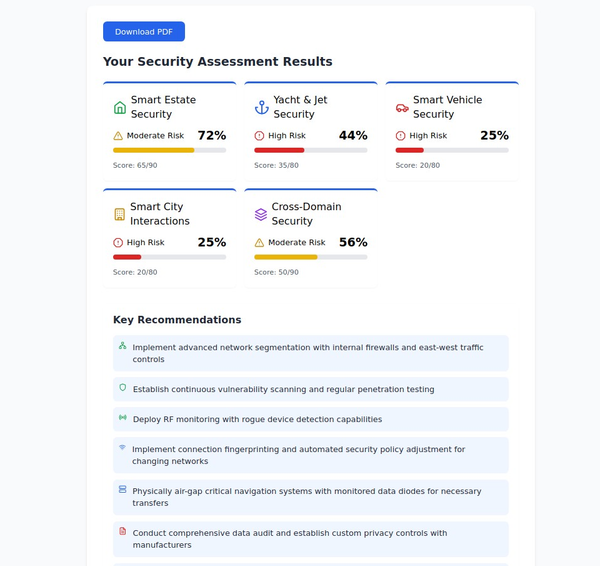
Integration of Smart Home Devices into Smart Cities
Smart home devices are an integral part of the broader concept of smart cities, where technology is leveraged to improve the efficiency, sustainability, and quality of urban living. Here are several ways in which smart home devices contribute to and integrate with smart city infrastructure:

1. Energy Management
- Smart Grids: Smart homes with devices like smart thermostats, smart meters, and energy-efficient appliances contribute to the functionality of smart grids. These grids use data from homes to balance energy supply and demand, reduce energy consumption during peak times, and integrate renewable energy sources more effectively (CyberSec Training).
- Demand Response Programs: Smart homes participate in demand response programs, where utilities incentivize homeowners to reduce or shift their energy usage during peak demand periods. This is facilitated by smart devices that can be automatically controlled to optimize energy usage (CyberSec Training).
2. Water Management
- Smart Water Meters: These devices provide real-time data on water usage, helping utilities to detect leaks, manage water supply more efficiently, and encourage conservation efforts. Smart homes equipped with these meters contribute to the overall water management strategy of smart cities (CyberSec Training).
3. Waste Management
- Smart Trash Bins: Some smart homes use smart trash bins that can notify city waste management services when they are full. This helps optimize collection routes and reduce operational costs, contributing to a more efficient waste management system (CyberSec Training).
4. Public Safety and Security
- Integrated Surveillance Systems: Smart home security devices like cameras and sensors can be integrated with city-wide surveillance systems to enhance public safety. For instance, video feeds from smart home cameras can be shared with local law enforcement during emergencies (CyberSec Training).
- Emergency Response: Smart smoke detectors and alarms in homes can be linked to city emergency response systems, ensuring faster response times during incidents such as fires or gas leaks (CyberSec Training).
5. Transportation and Mobility
- Smart Parking Solutions: Homes equipped with smart garage systems can integrate with city-wide smart parking solutions, providing real-time data on parking availability. This can help reduce traffic congestion and improve urban mobility (CyberSec Training).
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Stations: Smart homes with EV chargers contribute to the city’s EV infrastructure. These chargers can communicate with the grid to optimize charging times based on energy demand and availability (CyberSec Training).
6. Environmental Monitoring
- Air Quality Sensors: Smart homes equipped with air quality sensors can provide data that contributes to city-wide environmental monitoring efforts. This data helps in managing air quality and implementing policies to reduce pollution (CyberSec Training).
- Noise Monitoring: Similarly, noise sensors in smart homes can be used to monitor urban noise levels, aiding in the creation of quieter and more livable urban environments (CyberSec Training).
Benefits to Smart Cities
1. Enhanced Efficiency
Smart home devices enable more efficient use of resources, reducing waste and operational costs. For example, real-time energy consumption data helps in managing and distributing energy more effectively across the city (CyberSec Training) (Eviden).
2. Improved Quality of Life
The integration of smart home devices with city infrastructure enhances the quality of life by providing better services, improving safety, and creating a more sustainable urban environment (CyberSec Training) (Eviden).
3. Data-Driven Decision Making
The data collected from smart homes contribute to the city’s data analytics efforts, enabling data-driven decision-making for urban planning, resource management, and policy formulation (CyberSec Training) (Eviden).
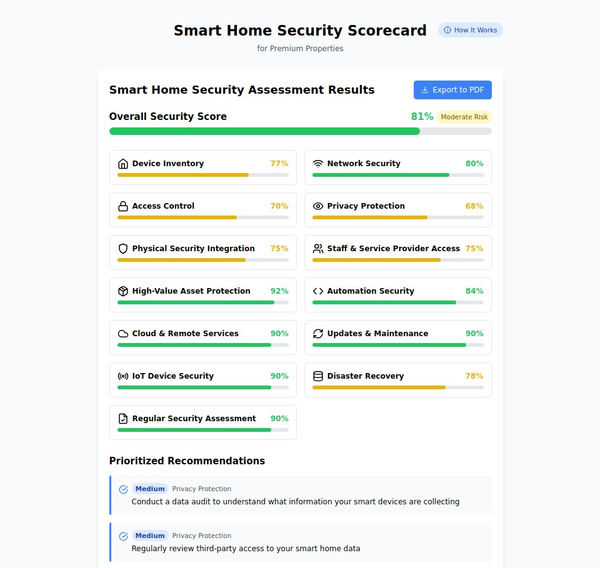
Privacy and Security Concerns
1. Data Privacy
With the extensive data collection from smart home devices, there are significant concerns about data privacy. Ensuring that data is collected, stored, and shared in compliance with privacy regulations is crucial (CyberSec Training) (Eviden).
2. Cybersecurity
Smart home devices connected to city infrastructure must be secure to prevent cyber attacks that could disrupt city services. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential to protect both individual homes and the broader city network (CyberSec Training) (Eviden).
Conclusion
Smart home devices play a crucial role in the development and functioning of smart cities. They enhance the efficiency, sustainability, and quality of urban living by integrating with various city systems. However, addressing data privacy and cybersecurity concerns is vital to ensure the safe and effective use of these technologies in creating smarter cities.
There have been several notable data privacy issues related to smart home hacking. Here are some examples:
1. Amazon Ring Cameras
- Incident: In 2020, multiple reports emerged of hackers gaining access to Amazon Ring cameras. Attackers used compromised credentials to access cameras, allowing them to watch live feeds and even communicate with homeowners and their children.
- Privacy Impact: Unauthorized surveillance and eavesdropping on private conversations, leading to significant privacy violations and emotional distress for the victims (CyberSec Training) (Eviden).
2. Google Nest Cameras
- Incident: In 2019, Google Nest cameras were hacked, allowing intruders to gain access to live feeds. Hackers used recycled passwords from other data breaches to log into Nest accounts.
- Privacy Impact: Intruders watched live footage of homeowners, communicated through the camera’s speakers, and in some cases, made threats. This raised serious concerns about the security of connected home devices and the privacy of users (CyberSec Training) (Eviden).
3. Smart TVs and Voice Assistants
- Incident: Smart TVs with built-in microphones and cameras, along with voice assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant, have been found to be vulnerable to hacking. Attackers can exploit these devices to listen in on conversations or watch users through the cameras.
- Privacy Impact: Unauthorized access to audio and video recordings can lead to significant privacy invasions, capturing sensitive and private moments of the users' lives (CyberSec Training).
4. Thermostat and Smart Appliance Hacks
- Incident: Vulnerabilities in smart thermostats and appliances have been exploited to gain unauthorized access to home networks. For instance, the Mirai botnet exploited weak security in IoT devices to launch DDoS attacks.
- Privacy Impact: While primarily used for launching attacks on other networks, the initial breach can expose the home network to further exploits, potentially compromising other connected devices and personal data stored on them (CyberSec Training) (Eviden).
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate these privacy issues, users should:
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Avoid using default or easily guessable passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of security for accessing smart home devices.
- Regularly Update Firmware: Ensure all devices have the latest security updates installed.
- Network Segmentation: Use a separate network for IoT devices to isolate them from personal data networks.
- Monitor Device Activity: Regularly check for unusual activity and unauthorized access to devices.
By taking these precautions, smart home users can better protect their privacy and secure their devices against potential hacking attempts.
Data Sharing Information of Smart Home IoT Devices with Authorities
Smart home IoT devices collect vast amounts of data that can be used for various purposes, including sharing with authorities under certain circumstances. Here are some key points regarding data sharing and privacy concerns:
1. Law Enforcement Requests
- Amazon Ring: Amazon has faced scrutiny for its partnerships with law enforcement agencies. The company has provided video footage from Ring cameras to police departments, sometimes without the owners' consent or a warrant. This has raised concerns about privacy and the potential for surveillance overreach (CyberSec Training) (Eviden).
- Google Nest: Google has also been known to comply with law enforcement requests for data from its Nest cameras and other smart home devices. This includes footage and other data that might be relevant to investigations.
2. Data Privacy Concerns
- Lack of Transparency: There have been complaints about the lack of transparency in how companies handle data requests from authorities. Users are often unaware of how frequently their data is shared or the specific circumstances under which it is handed over (CyberSec Training).
- Consent Issues: In many cases, users are not explicitly asked for consent before their data is shared with law enforcement, especially if the request comes with a legal mandate such as a subpoena or court order.
3. Regulatory and Legal Framework
- GDPR and CCPA: In regions with strong data protection regulations like the European Union's GDPR or California's CCPA, companies are required to be more transparent about data sharing practices. These regulations mandate that users must be informed about what data is collected and how it is used, including sharing with third parties (CyberSec Training).
- Lawful Access: Most jurisdictions allow for lawful access to data with proper legal procedures. Companies generally comply with valid legal requests to avoid penalties and legal repercussions.
4. User Control and Security
- Encryption: Some companies use end-to-end encryption for data stored and transmitted by IoT devices, which can limit unauthorized access. However, this can also complicate compliance with lawful access requests.
- User Notifications: While some companies notify users when their data is requested by authorities, this is not always the case. Policies on user notifications vary widely between companies and jurisdictions.
5. Examples of Data Sharing Practices
- Amazon Ring's Neighbors App: This app allows users to share footage with neighbors and local law enforcement. Critics argue that it can lead to racial profiling and unnecessary surveillance (CyberSec Training) (Eviden).
- Google's Transparency Reports: Google publishes transparency reports detailing the number of requests for user data they receive from governments and how they respond. This helps to some extent in providing transparency about data sharing practices.
Mitigation Strategies for Users
To better protect their privacy, users can:
- Review Privacy Policies: Understand the data sharing policies of IoT device manufacturers.
- Adjust Settings: Configure privacy and security settings on devices to limit data sharing.
- Use Encryption: Enable encryption features where available to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Stay Informed: Keep updated on the latest news and reports about how companies handle data requests and sharing practices.
Conclusion
While smart home IoT devices offer convenience and security, they also pose significant privacy concerns, especially regarding data sharing with authorities. Users should be aware of the potential for data sharing, understand their rights under relevant regulations, and take steps to protect their privacy.